- Neowise Comet Path
- Neowise Comet Orbit Diagram
- Neowise Comet Orbit Map
- Neowise Comet Orbit Path
- Comet Neowise Ephemeris
Last week I learned about Comet NEOWISE, the most impressive comet to pass by Earth in nearly 25 years. Since I didn’t recall ever before seeing a comet, I was more than happy to stay up late to catch a glimpse of it in the night sky. When I finally spotted it, I was inspired to learn more.
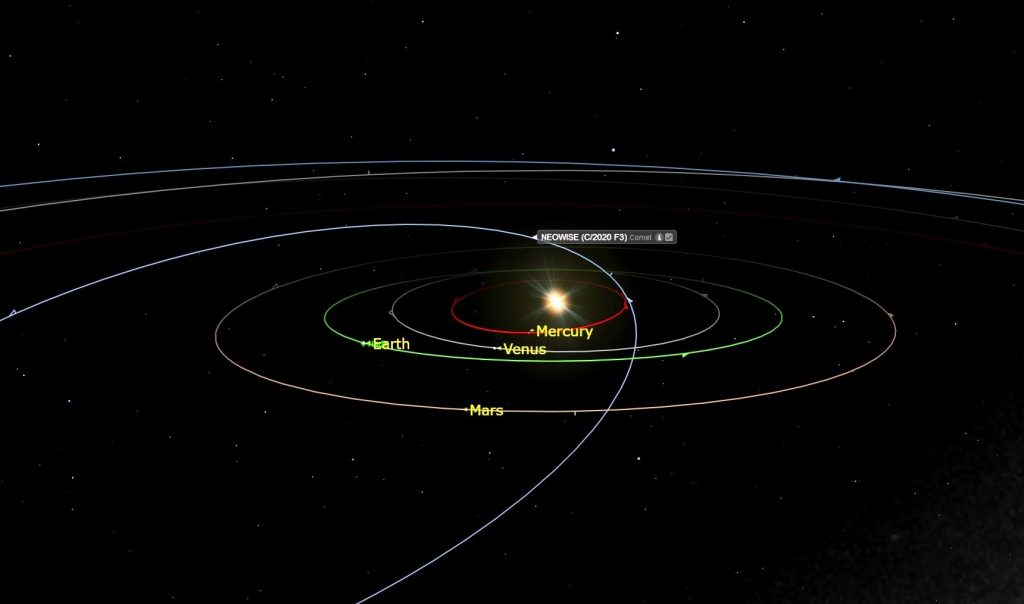
An online orrery, showing the positions of the planets and C/2020 F3 (NEOWISE) around their orbits. 3D Diagram of the orbit of C/2020 F3 (NEOWISE) - In-The-Sky.org In-The-Sky.org. Neowise has an orbit of almost 6,800 years, meaning that the last generation of people to see it would have lived during the fifth millennium BC. This was a time well before the written word, when.
After doing a little research online, I found out the comet was discovered on March 27, 2020 by a NASA space telescope. The telescope is called the Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE), which is where the comet got its name. However, since every comet discovered by this telescope is named NEOWISE, each one has a technical designation. This one is C/2020 F3.
Comet C/2020 F3 (NEOWISE) is a rare treat because it’s unusual for a comet to be bright enough to see with the naked eye. I first located it on July 16 by looking northwest, below the Big Dipper constellation. I stood outside for almost two hours searching the sky, and finally spotted it shortly before 11 p.m. MDT.
Interesting Facts about Comet NEOWISE
Comet NEOWISE is on a near parabolic orbit around the Sun. It passed closest to our big ball of fire on July 3. Now, it’s headed toward its nearest pass by Earth. On July 23 it will be a close as it’s going to get, at a distance of 64 million miles.
The highly condensed core of the comet is 3 miles across. It is traveling at approximately 40 miles per second, or 144,000 miles per hour. However, since it is so far away, its movement is not discernible from our vantage point.
Even so, just to provide a reference, the International Space Station travels at the speed of 17,150 mph, completing one trip around Earth every 92 minutes. I just happened to see it zipping by while I was waiting for the comet to appear, and wouldn’t have known what it was if my dad hadn’t told me.
If you want to see what Comet NEOWISE looks like from the International Space Station, check out this video (the comet will start to appear at the 3-minute mark).
Contemplating the Vastness of the Universe
If you missed seeing Comet NEOWISE for yourself, I’m sorry to say it will be 6,800 years before it returns from its trip deep into the outer Solar System. That’s a mighty long time for this magnificent hunk of ice to be hurling through space. While you’re waiting around for it to come back, you’ll have plenty of time to contemplate the vastness of the universe.
To get you started, did you know the light reflecting from Comet NEOWISE takes only 5 minutes to reach the earth? That’s not long at all compared to starlight. In the case of the Big Dipper, for example, the light from the nearest star takes 63 years to reach your eyes, and the light from the farthest star takes 210 years.
When you gaze at the Big Dipper and other constellations, if the fact that the light you see shining left its star long before you were born doesn’t amaze and impress you, I don’t know what will.
The Difference between Comets, Asteroids and Meteors
Learning about Comet NEOWISE birthed a desire in me to understand the difference between comets, meteors, and asteroids. So, I took a few minutes to educate myself. Here’s what I now know that I didn’t know before:
Comets are icy celestial bodies that orbit the Sun. They can break up or burn out at any moment.
Asteroids are rocky celestial bodies that orbit the Sun, which are too small to be called planets but are larger than the typically pebble-sized objects we call meteoroids.
Meteoroids are small pieces of debris that have broken off of asteroids or comets and are floating around in space.
Meteors are meteoroids that have entered the earth’s atmosphere and become visible when they burn up. What some people call Shooting Stars or Falling Stars are actually meteors.
Meteorites are meteors that have hit the earth and have come to rest on the earth’s surface.
Thought for the Week: The universe is so unfathomably vast, how much bigger and more awesome is the Creator of the universe!
Neowise Comet Path
Neowise Comet Orbit Diagram
Comets are solar system objects made up of ice, rock and dust. Right now, a newly-discovered one is speeding by Earth, providing excellent light shows for the planet’s people.
The ice-rock is called Neowise. It is the brightest comet to appear above the Northern Hemisphere in 25 years. Social media users in many countries have posted images they captured of Neowise, as it lit up the sky over their heads.
Comets are normally about 8 to 16 kilometers wide. But, as they travel near the sun, they heat up, releasing gas and dust. The comet expands to form a “glowing head that can be larger than a planet,” says the U.S. space agency NASA. The process also creates a sunlit “tail” of dust. It can stretch for millions of kilometers behind the comet.
Scientists say Neowise is believed to be about 5 kilometers across. It passed inside Mercury’s orbit on July 3, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory said in a statement. The close pass by the sun was “cooking” the comet’s outermost parts, causing a major release of gas and dust material. “And yet the comet has managed to survive this intense roasting,” the statement said.
The comet was named for NASA’s NEOWISE infrared space telescope, which discovered it in March. The NEOWISE project aims to search the skies for what scientists call near-Earth objects, or NEOs. Such objects include asteroids and comets that could come within 50 million kilometers of Earth’s orbit.
In this case, NASA said Neowise would pass by Earth “at a harmless distance of 103 million kilometers,” while giving astronomers a good chance to study its substance and structure.
Sky watchers may be able to see Neowise as it passes through the inner solar system. But “its nearness to the sun” could make sighting it difficult, NASA says.
Experts say people in the Northern Hemisphere - the part of Earth above the equator - should look toward the northwestern sky, just below the “Big Dipper” star group.
Until recently, the best time to see Neowise was about an hour before sunrise. This week, the comet began making its appearance in the evening sky shortly after sunset.
People have been able to see the head of the comet without the use of equipment. But devices like binoculars and telescopes are better for viewing the comet’s long tail.
Neowise is expected to be seeable across the Northern Hemisphere until mid-August. It will then start making its way back to the outer parts of the solar system.

NASA says it will be about 7,000 years before the comet returns. “So I wouldn’t suggest waiting for the next pass,” said Joe Masiero of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Astronauts on the International Space Station caught a good look at the bright ice-rock last week. NASA’s Bob Behnken captured an image of Neowise and shared the picture on social media.
It shows central Asia in the background, and part of the space station in the foreground. “Stars, cities, spaceships, and a comet!” Behnken tweeted from orbit.
I’m Bryan Lynn.
Bryan Lynn wrote this story for VOA Learning English, based on reports from The Associated Press and NASA. Caty Weaver was the editor.
Neowise Comet Orbit Map
We want to hear from you. Write to us in the Comments section, and visit our Facebook page.
Quiz - Comet ‘Neowise’ Provides Light Shows while Passing by Earth
Start the Quiz to find out
_____________________________________________
Words in This Story
glow – n. a soft, warm light
Neowise Comet Orbit Path
tail – n. the back part of something long
roast – v. to cook or dry with heat
asteroid – n. a rocky object that goes around the sun like a planet
view – v. to look at something
Comet Neowise Ephemeris
Related
